JenRees 6/18/23

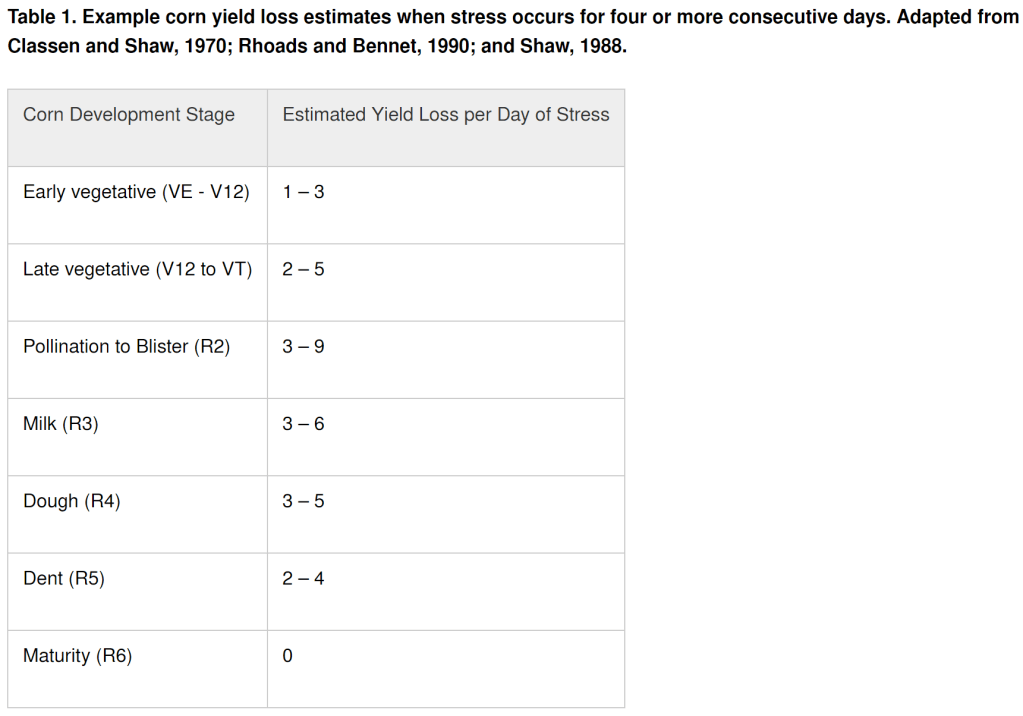
Drought: Several have asked about the yield potential of non-irrigated pivot corners if they were irrigated at this point. I don’t know if anyone really knows. This column reaches such a wide area. There’s part of the area I serve that I don’t think there’s any yield potential. For other places, my guess is ears wouldn’t be more than 4-8 rows around. I asked a plant breeder for his perspective. He shared it could be possible for 100-120 bu/ac with rain, depending on how long it had been rolled, and for corn further along (late vegetative stages). I’m seeing non-irrigated corn in most area drought-stressed fields are 4-7 leaf vs. 8-12 leaf in the pivot irrigated portion. The research I found says, from Emergence to 12 leaf corn, an estimated 1-3% yield loss occurs for each day after 4 consecutive days of stress. Some corn in the area has been rolled for nearly 18 days. Here’s some math for consideration if it can help (I’m going to use 20 days of stress). Let’s say you typically receive 180 bu/ac non-irrigated yield. 1% yield loss/day for 20 days would result in a loss of 36 bu/ac. A 2% yield loss/day for 20 days would result in a loss of 72 bu/ac and a 3% yield loss/day for 20 days would result in a loss of 108 bu/ac.


I’m honestly surprised that the drought-stressed corn is still gray-blue/green in color overall with only a few scattered plants firing now. I know it’s hard to see the corn dying. Each situation varies regarding well capacity and if there’s other wells to water corners, how long the corn has been stressed, etc. Overall, my suggestion has been to not divert water from pivots to save corners. For beans, they’re putting energy into deeper roots with less above-ground growth. These small beans will most likely flower shortly and yield loss will be from aborted flowers, pods, or death of plants if we don’t get rain.
Several have also commented on weed control difficulties with drought-stressed weeds. There’s two well-written articles in this week’s CropWatch https://cropwatch.unl.edu about drought-stressed weeds.
ET/GDD info: The CropWatch ET (evapotranspiration) info. is now available at: https://cropwatch.unl.edu/gdd-etdata.
2nd Cutting Alfalfa: Non-irrigated alfalfa fields are short (6-12”) with some blooming. Received a question regarding to cut or not. Dr. Bruce Anderson had shared in previous years that one needs to obtain at least 0.5 ton/acre in order to pay for harvesting costs. With higher hay prices and short forage, you can determine what’s best for your situation. Alfalfa that goes dormant will regrow when rains occur. By leaving it alone, the alfalfa will go dormant and eventually lose the leaves from the stems. If you hay or shred it, it may try to regrow, but with no moisture, it will also go dormant. There’s also potential to damage crowns from driving on extremely stressed alfalfa. If you can fence it and have water access, grazing full-bloomed alfalfa is also an option and is low-risk for bloat at that stage.
Lawn Watering: Lawns are really showing drought stress. Kentucky bluegrass is shallower-rooted and doesn’t take heat as well as fescue. However, bluegrass will go dormant without dying, whereas fescue, even though it’s deeper rooted and more drought-tolerant, doesn’t go dormant from drought-stress, so it can die. After bluegrass has reached three weeks of dormancy and fescue has changed color, it’s recommended to water 0.5”/week to keep both grass species from dying.
Oak Leaf Tatters: Received calls in the Henderson/Bradshaw area about oak trees with leaves that looked like they’d been eaten; no insects were present. Several calls earlier in the year were regarding malformed oak leaves, primarily on young oak trees (1-5 years old). Oak leaf tatters is a condition characterized by Iowa State, where cold stress when tree leaves are emerging coupled with herbicide injury causes oak leaves to look deformed, tattered, or look like they’ve been eaten. I see problems every year with oak trees, primarily in lawns when ‘weed and feed’ products are applied when oak tree leaves are emerging. So, in the future, avoid those products in lawns during leaf emergence. There were also some late cold snaps that likely impacted oak trees when leaves were ready to emerge. There’s nothing to do other than to water to avoid drought stress. All the trees I looked at are developing new growth; they’ll look more ‘normal’ in 10-14 days. The cold snaps may have also impacted apple and other fruit tree varieties that were in the pink/white bud stage or already starting to bloom, thus why some trees don’t have fruit.



Please take care of yourselves! Rural Wellness website: https://ruralwellness.unl.edu/ and Nebraska Rural Response Hotline: 1-800-464-0258.
Posted on June 18, 2023, in Drought, JenREES Columns, Lawns, Trees and tagged drought, drought 2023, drought yield impacts, irrigating lawns, oak leaf tatters. Bookmark the permalink. Leave a comment.

Leave a comment
Comments 0