Monthly Archives: November 2025
Reflections on Gratitude
With the growing season ending and the transition to winter programming beginning, I’ve been reflecting on gratitude, and the gifts of time, health, relationships, and seasons.
My husband and I, along with many of you, were so grateful to finish this harvest season! In spite of disappointing yields, I heard several farmers say they were looking forward to gathering with family on Thanksgiving and counting their blessings. That’s a great attitude as we are truly so blessed!
Regarding seasons, I’m ironically finding much gratitude in the nights turning darker earlier to allow for rest on the farm. You don’t have to agree; I truly believe that’s a gift God gave to us in farming communities who go so hard most of the time. The beauty found in each season was recognized by a beautiful, warm day last Sunday and white snow against green evergreens this Sunday!
Many family and friends in my life are struggling with health concerns; most likely in yours too. It’s daily reminded me how easy it is to take health for granted and be grateful for the health I have. Health is more than just physical; it’s also mental, emotional and spiritual. Life is so short and not guaranteed! Relationships are so important and can be fragile. This led me to think about relationships in my life and the need to be intentional in giving time to others. It’s so easy to be “busy” but are we “busy about the right things”? I’ve written names of people to connect with and now need to be intentional in doing that. What about you? Are there people in your life who could benefit from the gift of intentional time spent catching up?
As I reflect on this year and walk alongside of people, it seems like there’s increasing divisiveness, uncertainty, fear, anxiety, depression, and stress. For encouragement, fear and anxiety can’t succeed in the midst of gratitude. Gratitude produces Joy! When we focus on gratitude and choose joy, there’s no room for worry, discontentment, or fear for the focus is no longer on ourselves.
If we chose to live with gratitude, how would it change us and our perspectives? Would we be less prone to complain and get discouraged when things go wrong? Would we be less likely to argue and more likely to extend kindness and grace to others? How would it impact the divisiveness we see in our country, our communities, our families?
So how do we choose to live with gratitude? A start can be to intentionally seek at least one thing each day for which to be thankful. At first it can be difficult and perhaps awkward. For some, it’s hard to even think of one thing. Perhaps a starting point can be gratitude for one’s home, bed, food, vehicle, job, friend or family member, etc.? Over time of practicing this, one’s perspective can change to even finding gratitude as things go wrong. I’m not good about this all the time, but it sure helps my mindset and increases my perspective when I choose gratitude even when things go wrong. Perhaps others can relate to this?
Ultimately, my hope is that we can experience more joy each day in the everyday moments as we intentionally seek to live with gratitude. And, that this joy can be extended via kindness, grace, compassion to others around us.
Reminder of several programs this week: Organic Conference Dec. 2 near Mead, Dr. Kohl at 1 p.m. at the Bruning Opera House on Dec. 3, and the Landlord/Tenant cash rent workshop at 10:30 a.m. at the Seward Co. Extension Office on Dec. 4.




JenResources 11/24/25
Wishing everyone a blessed Thanksgiving! Here are some Thanksgiving food safety tips, recipes, and wellness activities from UNL Extension Food faculty: https://food.unl.edu/article/thanksgiving-central/.
Nitrogen Reduction Incentive Act Deadline has been extended to December 15, 2026. With a late harvest, this will help producers who desired to get an application in to try a practice on their farms that would reduce nitrogen rates by 40 lb N/ac. The online application form can be found at: https://app.smartsheet.com/b/form/090982880f3e47c196a83ea1928158c7. Additional information regarding this program can be found at: https://dnr.nebraska.gov/lb-1368-nitrogen-reduction-incentive-program.
Organic Conference: Are you interested in learning more about organic farming, are in the transition process or are already a certified organic producer? We invite you to join us for our third annual “Transition to Organic Farming” conference on December 2, 2025, at the Eastern Nebraska Research and Extension Center near Mead. This is a great event that brings together producers, extension, industry, non-profits, and researchers. Online registration is now open and is free due to funding from our sponsors, the USDA Transition to Organic Partnership Program (TOPP) and Nebraska Extension. Click here to register: https://enreec.unl.edu/2025-transition-to-organic-farming-conference/.
Farmers & Ranchers College: The Agricultural Update and the Road Ahead with Dr. David Kohl will be held on December 3, 2025, at the Opera House in Bruning, NE at 1:00 p.m. There is no charge for this program due to the support of the Farmers and Ranchers College sponsors. This session will connect the dots between today’s economic landscape and your business decisions on the ground. Practical financial and management strategies will be shared to help you adapt, lead, and succeed, regardless of the economic cycle. This is versatile for a wide range of groups including lenders, producers, agribusiness owners, and students. More info. at: go.unl.edu/farmersrancherscollege.
Landlord/Tenant Cash Lease Workshop in Seward December 4 will be held for landowners and operators from 10:30 a.m. to 2 p.m. Dec. 4, at the Extension Office in Seward, 322 S. 14th St. The meeting, titled “Financial Strategies for Effective Agricultural Land Leasing and Management” will cover current Nebraska cash rental rates and land values, best practices for agricultural leases, and other contract considerations. The meeting will also include financial considerations for farm succession and transition and offer an opportunity for those in attendance to have their leasing questions answered. Lunch will be provided, sponsored by Farmers National Company. There is no charge to attend, but registration is required by Dec. 3 by calling the Extension Office at 402-643-2981. More information about cash rental rates, leasing and farm and ranch transition can be found on the Center for Agricultural Profitability’s website, https://cap.unl.edu.


2025 Yields Part 2
York County Corn Grower Banquet will be held Thursday, November 20th at Chances ‘R in York. Social at 6:30 p.m. with meal at 7 p.m. Tickets are $20 and can be reserved at the Extension Office at (402) 362-5508 or contacting a York Co. Corn Grower Director.
In last week’s column, we walked through the growing season providing perspectives of what may have caused yield loss. I mentioned that while people are looking for solutions, increased nitrogen rates, more fungicide applications, and tillage are not the answers for higher yields. In conversations, those were the “solutions” people were trying to provide. Several asked me for any patterns from observations and conversations I’ve had. That’s what I will attempt to share in this column. There’s a number of field situations where only 150 lb N and one fungicide application resulted in above-average yields. In those situations, correlations included balanced overall nutrition where nitrogen was reduced, TIMELY fungicide application, and not over-irrigating.
I realize quite a bit of tillage has occurred. Gently, please remember the wind events we receive each spring. I encourage you if you have tilled, to consider covering the ground with cereal rye. March 2025 was the windiest March on record in Nebraska and I remember several accidents due to poor visibility. I realize this is a hard topic. Tillage will not control southern rust as that fungus doesn’t overwinter in residue. It will help with the tar spot fungus, but there are other management considerations including hybrid and not over-applying nitrogen and irrigation.
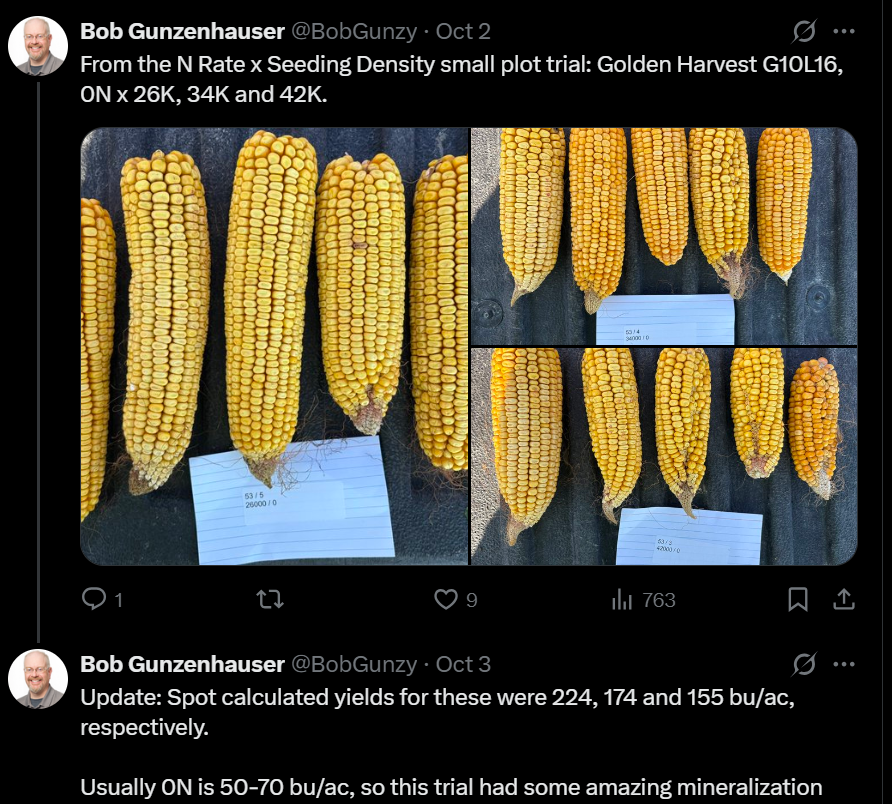
Reduced nitrogen: It was interesting walking our on-farm research studies where we had nitrogen ramps this past year and observe the correlation between less southern rust in the lower nitrogen rates and more southern rust in the higher nitrogen rates. Dr. Bob Gunzenhauser observed the same thing this past year and posted a photo on X showing two hybrids and the variation of southern rust compared to nitrogen rates.

Timely fungicide application: There were people with better yields (250+) who applied only one fungicide while others applied two. I didn’t hear too much from those who applied three to five applications. Some applied two fungicide timings of two different generic products and did just as well as the higher priced products with one application. The key was not applying the fungicide too early so there was some later season residual. Some applied a second fungicide around late dough to early dent stage this year and that seemed to work for hybrids that were more prone to southern rust. The keys were knowing the hybrid, not having excess nitrogen, and proper irrigation management.
Irrigation Management was perhaps the thing that was most frustrating for growers. We started the season off so dry after several years of being dry. So, it’s easy to be in the mindset of irrigating. Anytime non-irrigated fields yield the same or more than irrigated fields, it’s often due to over-irrigation. Irrigation events often occurred before rain events this year. This year’s relative humidity was also very high, thus, the crop didn’t use as much water. Because of that, we were keeping some soils too wet by irrigating which, both Dr. Tom Hoegemeyer and I believe, added to the crown rot and stalk rot issues we experienced. Dr. Hoegemeyer also wrote a recent article reflecting on “60 Harvests – Changes I Have Seen — Nebraska Soil Health Coalition“.
Final thoughts, there’s not one answer but a combination of factors that impacted fields this year. There’s also a lot of farmers hurting with the combination of low yields, low commodity prices and high input costs. Hundreds of thousands of dollars were lost per field in several situations. For those involved and/or interacting with the farming community, please reach out to each other and check in with each other. Please know you’re not alone and there’s always help and hope if you’re struggling. 988 is Nebraska’s suicide and crisis lifeline. There’s also a number of people who have announced retirements or will be announcing them. It’s important to be supportive. Conversations I’ve had with growers this year include: retiring to avoid taking on additional debt, wanting to scale back to reduce debt and stress, and retiring due to health reasons-both physically and anxiety/stress. It’s important for those retiring to retire “to something” by staying active in some way.



2025 Yields
This harvest was a difficult one, plagued with breakdowns, slow-going in storm-damaged corn, and disappointing yields. While there were a few reports of decent yields, the overwhelming majority of farmers and seed dealers in the area have been disappointed. Honestly, I was worn down and needed a mental break before I could address this in writing. I asked Dr. Roger Elmore, Dr. Tom Hoegemeyer, Dr. Bob Nielsen, and Dr. Eric Hunt if my reasoning was on track and for their additional thoughts and am grateful to them.
Major Point: People are looking for solutions, but increased nitrogen rates, more fungicide applications, and tillage are not the answers. What went right? Balanced nutrient management with reduced nitrogen inputs, TIMELY fungicide application, and proper irrigation management are future keys.
We began the season with dry planting conditions. I was arguing we were potentially drier than Spring 2023 with the observations about rye and pastures not growing. Crops went into the ground quickly without cold snaps. Several farmers were completely done planting in April. Irrigation began early to get moisture into seedbeds and to activate herbicide. Plant stands and emergence were uneven, evidenced again at harvest with varying ear sizes and plants with ears that didn’t pollinate. I think that impacted us more than we realized. The Memorial Day weekend rains saved us.
A relief was that rain kept falling in spite of it varying greatly in timing and amounts. Some experienced higher non-irrigated yields in corn and soybeans compared to irrigated fields. That nearly always is due to too much irrigation and timing of those irrigations, often occurring right before a significant rain event.
We had a few wind/hailstorms in July and the fairly widespread Aug. 8-10 wind/hail event, which York Co. escaped. Much of the year we received lower than average solar radiation (which includes photosynthetically active radiation or PAR). There were several periods of cloudy/hazy/smoky days. Research utilizing shade cloth revealed 25-30% potential yield loss with shading occurring from R2-R6 stages in corn. As Dr. Roger Elmore pointed out, the hybrid maize model was predicting average yields at the end of the growing season in spite of the low PAR, which would suggest biotic (living) factors being the greater issue. Photosynthetic stress on plants can also include southern rust impacts on leaf tissue and stalk rots. I’m wondering if irrigation prior to heavy rain events exacerbated the fusarium crown rot/gibberella stalk rot we saw? Dr. Tom Hoegemeyer wondered the same thing. “Photosynthetic stress and stalk rot go together like beans and weenies. Each one can cause the other. We MAY have had some early infection with Fusarium/gib due to saturated soils/etc. As you know, high N rates, lower K available and a dozen other stress sources make it worse.”
High night-time temperatures burn sugars that should go into ears to fill kernels. I mentioned my concern about this throughout July and August. By mid to late August, ears began pre-maturely drooping, cutting off the food supply to kernels. Looking at kernels in numerous fields at harvest time, they appeared shriveled/pinched at the base. Dr.’s Tom Hoegemeyer, Roger Elmore, and Bob Nielsen all attribute that to stress occurring before black layer in which the kernels prematurely died before completing the normal black layer process. I feel the greatest contributors of this were the high night-time temperatures and the stresses of southern rust and stalk rots. Dr. Eric Hunt also mentioned the high humidity, particularly in York County due to the sheer amount of irrigation which may have led to increased disease pressure including stalk rots.
Dr. Bob Nielsen: “Your description of the kernels makes me think that kernel development was prematurely halted. Although, honestly, severe reductions in photosynthetic leaf tissue prior to BL (black layer) due to southern rust etc. or early onset of severe stalk rots would also prematurely shut down kernel development. And, of course,…(large) ears with excellent kernel set create a huge demand for photosynthate during grain fill, which exacerbates the negative effects of severe loss of photosynthetic leaf tissue and predisposes the stalk and root tissue to rapid fungal rot infection and development.”
Dr. Tom Hoegemeyer summed it up: “I think we had lots of issues that caused PS (photosynthetic) stress, some of which impacted our irrigated acres worse than our dryland acres. (My home dryland area had lots of 200 to 220 bpa corn and 65 to 70 bpa soybeans. After a dry spring, we had more rain than we’ve had for years). Irrigated corn in the area often wasn’t as good as the dryland, even with more N applied. The more stressors (hot nights, light limitations, too high N for the amt of light/PS–exacerbating disease issues, multiple leaf diseases combined with high humidity, continuous corn, etc.) the bigger the yield loss. And, in some instances, I think adding water to these fields hurt more than it helped.”




Sources:

York: -21 MJ/m2
Grand Island: -9.7 MJ/m2
Lincoln: -25.2 MJ/m2
Falls City: -28.3 MJ/m2
Norfolk: -10.7 MJ/m2
Wayne: +19.7 MJ/m2
West Point: -1.3 MJ/m2″



Southern Rust Myths
The following article, originally published in CropWatch (https://cropwatch.unl.edu/mythbusters-southern-rust-edition/) , was written by Dr. Tamra Jackson-Ziems and Kyle Broderick. High disease levels of southern rust were present in 2025, impacting yields. This article addresses the misinformation we are hearing about southern rust before decisions are made for next year’s growing season.
“Myth #1: Overwintering Rust: The southern rust fungus cannot overwinter in Nebraska. (It cannot survive in corn residue or soil).
The southern rust fungus (Puccinia polysora) needs to infect living, green corn in order to survive, and there is no known alternate host. Thus, the fungus can’t overwinter anywhere the climate doesn’t support corn growth through the winter months.
In fact, our rust fungi are likely blown north into the United States from subtropical locations, such as parts of Mexico, where corn is grown year-round. The southern rust fungi typically reach Nebraska in late July; however, this year they arrived earlier than usual, with the first confirmed sighting on July 9 — the earliest on record for the state.
Myth #2: Infected Grass: Southern rust doesn’t infect brome or other grasses nearby.
Rust fungi tend to have very narrow host ranges, infecting only one or a few plant species. Because several species of rust thrive under the same environmental conditions, it’s not unusual to see multiple plant species showing rust symptoms at the same time — even though they’re caused by different pathogens.
Myth #3: Super Strains: There is no new “super strain” of southern rust fungus.
… the severity we observed was due to prolonged periods of extremely favorable weather conditions — southern rust thrived under high relative humidity and average temperatures around 80°F. Southern rust…has been confirmed in 19 of the last 20 years…. If you remember 2006, you might recall another historic outbreak centered in south-central Nebraska. That season also brought delayed corn planting from spring rains, followed by ideal weather for rust development during the first two weeks of August. Many fields suffered stalk weakening and lodging, which caused memorable harvest challenges.
Myth #4: Fungicide Failures: Fungicides did not fail to control southern rust this year.
Although yield data are still coming in, most reports indicate that fungicides performed wellagainst southern rust this year. During years with substantial disease pressure, differences in fungicide performance become more apparent, underscoring the importance of selecting effective products and applying them at the right time. Results from multiple states, compiled by the Crop Protection Network, reinforce these findings. Remember: Even the best product can’t perform well without good coverage and proper timing, especially in a season like 2025 when disease pressure was unusually high.” The full article can be viewed at: https://cropwatch.unl.edu/mythbusters-southern-rust-edition/.






