2017 Ag Day
Happy Ag Day (March 21) and National Ag Week! 
The Agricultural Council of America began celebrating Ag Day in 1973 with the desire to recognize and celebrate the contribution of agriculture in our everyday lives. This program encourages every American to understand how food and fiber products are produced; value the essential role of agriculture in maintaining a strong economy; and appreciate the role agriculture plays in providing safe, abundant, and affordable products.
Today, each American farmer feeds more than 168 people which is a large increase from 25 people in the 1960s.
Today’s farmers also produce 262 percent more food with 2 percent fewer inputs (labor, seeds, feed, fertilizer, etc.), compared with 1950. Farm and ranch families comprise just two percent of the U.S. population. According to the American Farm Bureau Federation, America’s rural landscape is comprised of around 2 million farms with 99 percent of U.S. farms being operated by families – individuals, family partnerships or family corporations. Farmers on average receive only $0.13 of every dollar spent on food at home and away from home.
Regarding Nebraska, the Nebraska Department of Ag reports in its “2016 Ag Facts” card that cash receipts contributed almost $23 billion to Nebraska’s economy in 2015 and 6.1 percent of the U.S. total.
- Nebraska’s ten leading commodities (in order of value) for 2015 cash receipts are cattle and calves, corn, soybeans, hogs, chicken eggs, dairy products, wheat, hay, dry beans and potatoes.
- Every dollar in agricultural exports generates $1.22 in economic activities such as transportation, financing, warehousing and production.
- Nebraska’s $6.4 billion in agricultural exports in 2015 translates into $7.8 billion in additional economic activity.
- Nebraska’s top five agricultural exports in 2015 were soybeans, feeds and fodders, beef and veal, corn and soybean meal.
- Nebraska had 48,700 farms and ranches during 2015; the average operation consisted of 928 acres.
- In 2015, Nebraska had 25 operating ethanol plants with a total production capacity of over 2 billion gallons. Nebraska ranked 2nd among states in ethanol production and utilized 31% of the state’s 2015 corn crop.
- Livestock or poultry operations were found on 49% of Nebraska farms.
- 1 in 4 jobs in Nebraska is related to agriculture.
- From east to west, Nebraska experiences a 4,584 foot elevation difference and the average annual precipitation decreases by one inch every 25 miles.
- Between 2007-2012, Nebraska experienced a 5% increase in the number of farms and 10% increase in the number of new farmers.
So agriculture is of huge importance to our economy! It was interesting to see the change in some of these numbers compared to last year, a sign of the economic times we currently face in the agricultural industry. Information is being shared each week at our CropWatch web site to help.
Please be sure to thank a farmer and those who work in the agricultural industry this week! Without them, we wouldn’t be able to enjoy the safe, affordable, healthy food supply and choice we have as consumers!
Ag and Flex Lease Workshop
Cash lease questions are continually one of the top questions I answer in the office. We’d encourage landlords, tenants, and spouses to attend this or a workshop near you to hear the most updated information for the coming year!

Grubs — Husker Hort
Happy Summer! June 20th marked the start of the summer season. Summer means a good time for cookouts, picnics, swimming, and grub control. Not exactly what you had in mind for summer fun? Knowing the pest and its habits can help keep you from spending all of your summer fun time dealing with grubs.
Youth Crop Scouting Competition — Views from VanDeWalle
Connecting Youth with Crops… Looking for a fun club project? Want to unite your club members? Running out of ideas for club meetings? If you answered, “yes” to any of these questions, help is on the way! Nebraska Extension is pleased to present the 3rd annual Crop Scouting Competition for Nebraska youth. Youth interested in […]
Crop Updates-May 2016
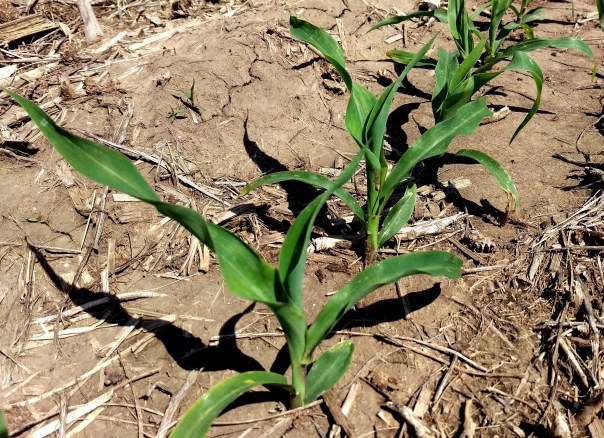

May 27: Sunshine has been welcomed for corn amidst the rains we’ve received. Corn ranges from 1-4 leaf depending on emergence dates. For those who put the majority of nitrogen application pre-plant, soil and/or foliar samples may be necessary to determine the extent of nitrogen available to the crop throughout the season.
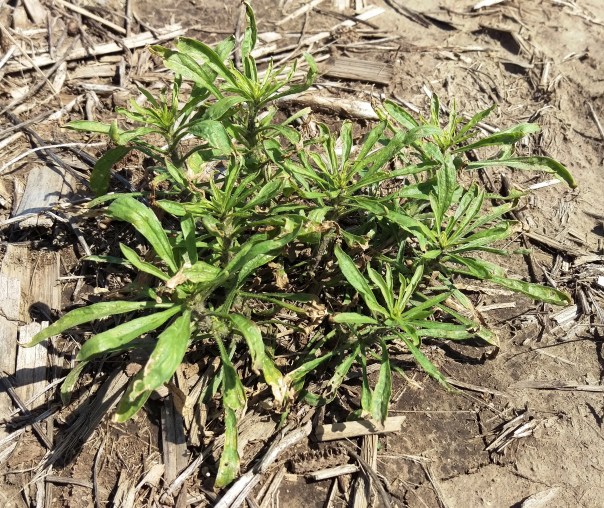

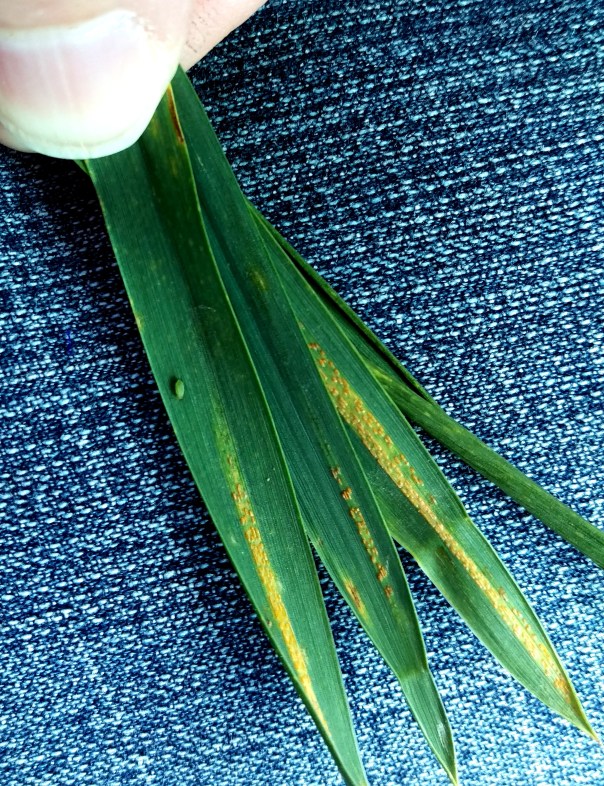
May 27: Receiving numerous calls on marestail escapes in corn this year. At this point, there’s no options guaranteed for 100% control. Our Guide for Weed Management shows options for 80% control right now including: Buctril + atrazine, Buctril + dicamba, Hornet, Realm Q, Resolve SG/Solida or Resolve Q, and Status. Please read and follow all label instructions. For soybeans, options are even more limited and control mostly goes down to 70%. Page 116 of our Guide for Weed Management provides options for consideration.
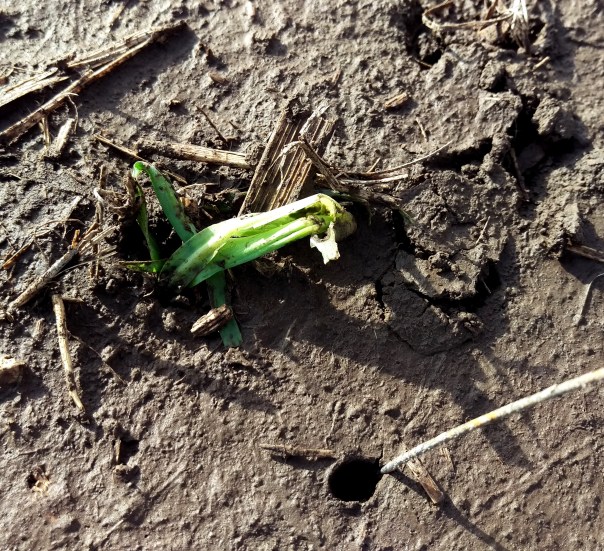

May 27: Also was called to a field for unique situation to me. Field had been two years of soybeans before planted to corn this year and had received hail 2 days before and over 4″ of rain within a few day period. Night crawler trails and holes the diameter of pencils existed throughout the field. The hail-stripped leaves were being moved down into holes. Where the stripped leaves were still attached to plants, the entire plant was bent over into the holes. It’s a unique situation in which the corn will hopefully outgrow with warm weather and sun. This unique occurrence is also mentioned at the following Purdue University website: http://extension.entm.purdue.edu/pestcrop/2010/issue9/index.html
May 23: Corn is looking good for the most part with few major concerns yet. Some have commented on the yellow-looking corn. This is most likely due to cool, wet soils rather than any nutrient issues. There may be field-specific issues such as saturated soils, compaction, and some herbicides that can cause this yellowing too. Also had a call on cutworms in seed corn but not widespread calls on this yet. Extension Educators have set up light traps for tracking cutworm moths and you can find that information here: http://go.unl.edu/rhhe. Cutworms will cause the most damage the first 7 days after corn emergence so scouting is important. The York County Corn Grower Plot was planted on April 24th with the corn currently at 2 leaf stage. Special thanks to Ron, Ray, and Brad Makovicka for hosting and the work put into this plot each year!

May 23: Soybeans are emerging and the concern several have discussed is crusting. Soybeans have an amazing ability to push through crusted soil and we were hoping for rains this past weekend to soften the soil and help them along. I’ve watched soybeans lose both cotyledons when trying to push up through the soil. Surprisingly these can survive if the growing point is still intact, and a small plumule will begin to develop.
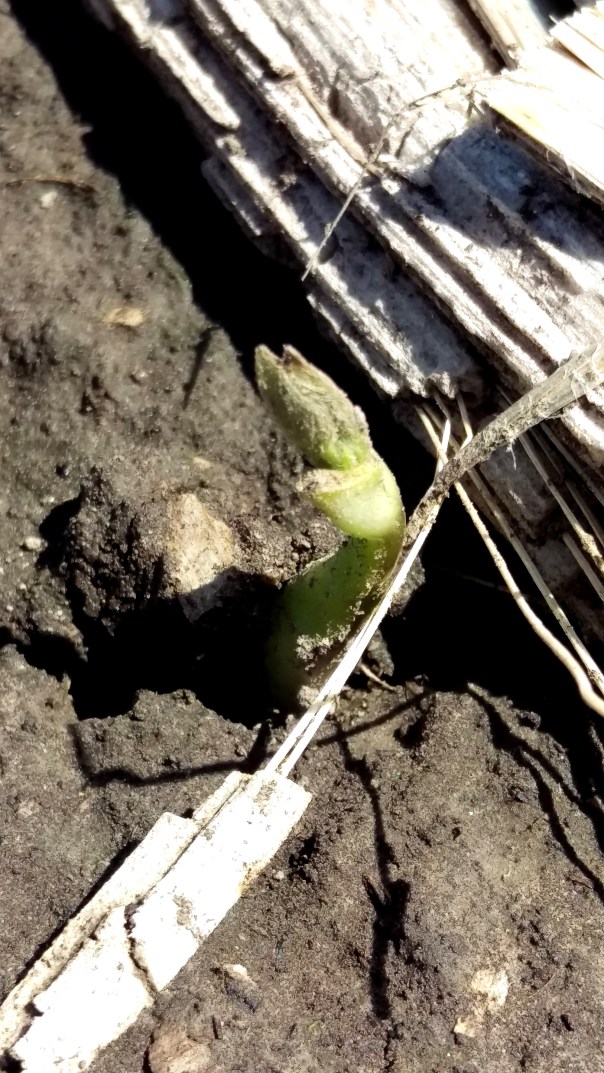

The plumule, which is the seedling stem tip and its undeveloped leaves above the cotyledonary node, may remain, but without the cotyledons to serve as a carbon and nitrogen source, development of new seedlings with small leaflets will be slow. These plants may not become competitive with surrounding plants. Therefore, when counting seedlings to determine plant stand after a soil crusting event, count only the seedlings that have at least one cotyledon. You can count seedlings missing cotyledons if they have large unifoliolate leaves that will soon unroll. Information from Purdue University shows that losing both cotyledons can lead to 2-5% yield loss.

May 15: After last week’s storms, some have wondered how long their germinated seed and emerged plants could survive under water. There isn’t a great deal of research regarding germinated corn hybrid seed. From some corn inbred research, it is not expected that germinated seed can survive in flooded conditions for more than four days. Within 48 hours, soil oxygen becomes depleted and crusted soils from heavy rains can lead to reduced emergence. A two day flooding event after soybean seed germination and imbibition (water uptake) reduced soybean stands from 20-43% in research conducted in the early 2000s. Corn less than 6 leaf growth stage at temperatures less than 77F can survive around four days. Temperatures higher than 77F may only allow those emerged plants to survive around 24 hours. As waters recede and for those who received hail on young corn, it will be important to monitor your plant stand. The high rains received early May 2015 in Nuckolls and Thayer counties resulted in a number of early corn diseases including bacterial soft rot and systemic goss’ wilt which reduced plant stands. We also saw an onset of anthracnose and a Xanthomonas bacterial disease that we couldn’t do anything about. Correct diagnosis will also be important. We would recommend monitoring your plant stand in ten areas of your field, counting plants from two adjacent rows in each area and assessing the distance of gaps between plants. Digging in the areas where gaps occur can help determine if seedlings still have an opportunity to survive. Seedlings that have leafed out underground or are corkscrewed will most likely not develop normally and may never make it out of the ground; it’s a judgement call on your part. An article is also provided in CropWatch this week to help with stand assessment for corn replant decisions at: http://go.unl.edu/iic6. One thing to keep in mind with the final decision table from Iowa State is that it all rests on an assumption of optimum planting of 35,000 seeds/acre planted in a window between April 20-May 5. That may or may not be a realistic assumption for your field conditions. Another thing to keep in mind is that while on average, as planting dates move into May, corn yields tend to drop, 2016 may not be an average year and the best planting date for 2016 with the weather conditions we’ve had may not have been the earliest ones. Regarding gaps, ISU shares gaps from 1.3-2.8 feet result in an additional 2% yield reduction while 4-6 foot caps result in an additional 5% yield reduction.
May 1: It never ceases to amaze me how quickly planting occurs each year! Corn planted the week of April 10th has emerged and for those fields that received hail from last week’s storms, I’m hoping we don’t see disease issues later on. Also of note, some have asked me about the CropWatch soil temperatures as they are higher than what some of you have been measuring in your fields before planting. The CropWatch soil temps at http://cropwatch.unl.edu/cropwatchsoiltemperature are averages of 24 hours under bare soil which may be different than the residue conditions in your fields and is an average of the entire day vs. one point in time. This may help explain some of the differences.
Many stands of alfalfa are lush green with over a foot of growth at this point. I looked at some alfalfa in Clay County that got dinged by cold temperatures in areas of the field and stopped growing. At this time I’m also finding quite a few aphids and a few alfalfa weevils. A disease common this time of year called spring black stem can be observed in nearly all alfalfa fields right now in the lower canopies. This disease consists of small black lesions on the leaves which eventually cause the leaves to turn yellow and drop. Normally this disappears with later cuttings as humidity and rainfall are typically high during the first cutting and can be managed with cutting the alfalfa. One option to consider according to Dr. Bruce Anderson, our Extension Forage Specialist, is to consider cutting alfalfa before bloom. He shares that weather can cause long delays and alfalfa doesn’t bloom very aggressively during spring. Bruce felt there were advantages to cutting alfalfa when it is 15-20” tall before bloom during first cutting including: weather compared to later spring, spread out alfalfa harvest if you consider cutting one field earlier, reduction in insect and disease problems by early harvest, and high feed value. It also potentially allows the second cutting to be ready before the summer heat which can lower forage quality. Disadvantages include lower yield from cutting early which could be made up in later harvest, regrowth may be slower if cut early, and the need to allow for longer recovery after first or second cutting to maintain long-term stands. So, harvesting before bloom may be something you wish to test in one of your fields this year and consider how this works for you, especially if you did have some frost damage or are having insect/disease issues in your alfalfa right now.